Licensing, RBAC Controls and Endpoint Protection Fundamentals in Intune
Why licensing matters
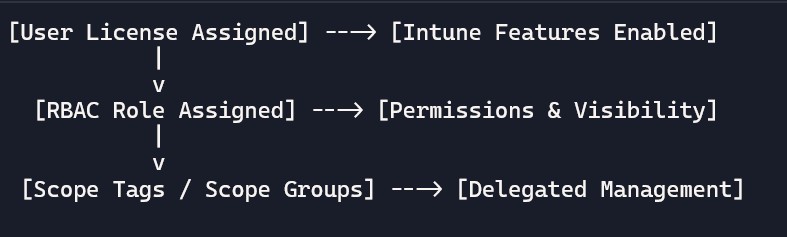
Licenses enable Intune features for users/devices. No license → no management. Make sure your licensing matches your needs (e.g., MDM, MAM, Endpoint Security, advanced analytics).
- Common license families:
- Microsoft 365 E3/E5 (includes Intune capabilities).
- Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS) E3/E5 (Intune + advanced security).
- Microsoft 365 Business Premium (SMB-focused, includes Intune).
- Per-user licensing: The user must be assigned a license for app protection and most device management scenarios.
- BYOD vs. corporate: BYOD might rely on App Protection Policies only; corporate devices typically use full MDM.
Role-based access control (RBAC) in Intune
RBAC defines what admins can see and do. Use least privilege to reduce risk.
- Global administrator: Full control across Microsoft 365 and Entra ID.
- Intune service administrator: Full control within Intune; limited outside.
- Help Desk operator: Can perform limited tasks (e.g., reset passwords, wipe devices).
- Application manager: Manage apps and assignments.
- Policy and profile manager: Create/assign device configuration policies.
- Security administrator: Manage endpoint security, baselines, and integrations.
Scoping and assignments
- Scope tags: Label objects (profiles, apps) for geography/business unit; restrict visibility.
- Scope groups: Define which devices/users an admin role can manage.
- Delegation example: India IT team sees and manages “India” devices only; US team manages “US” devices.
Best practices for licensing and RBAC
- License only active users: Reclaim licenses from leavers.
- Follow least privilege: Don’t grant global admin unless necessary.
- Document role responsibilities: Who creates policies? Who approves changes?
- Use scope tags consistently: Match org structure, avoid “miscellaneous” tags.
- Audit regularly: Review role assignments and changes quarterly.
Sample diagram: licensing and RBAC flow
Endpoint Protection Fundamentals in Intune
Endpoints are user-facing devices (laptops, mobiles). Intune protects them via Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) integration with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, security baselines, and attack surface reduction rules.
Layered Protection Details
- Device Protection: Firewall profiles (block inbound ports 135,445), BitLocker encryption (100% disk encryption).
- App Protection: PIN/biometrics for apps, data leakage prevention (no save to personal Dropbox).
- Data Protection: Selective wipe (remove company data only), encryption keys managed in cloud.
- Security Baselines: 5 baselines (e.g., MDM baseline with 44 settings like “Disable Cortana”).
Platform-Specific Features:
| Platform | Key Protections | Example Setting |
| Windows | Defender Antivirus, Exploit Guard | Block Office macros |
| iOS/Android | Jailbreak detection, App sandboxing | Require 6-digit PIN |
| macOS | Gatekeeper, FileVault | System Extensions blocklist |
Example scenarios
- Scenario – Helpdesk action: A Helpdesk operator can “Remote Wipe (Company Data)” on a lost phone, but cannot change Conditional Access policies.
- Scenario – App manager: Can add Outlook and Teams, assign to “All Users”, but cannot modify device compliance settings.
FAQ Section:
- Do I need a license to use Intune?
Yes, users must have a Microsoft 365 or EMS license that includes Intune. - What’s the difference between E3 and E5 licenses?
E5 includes advanced security and analytics features beyond E3. - Can I manage devices without assigning a license?
No, licenses are required for policy enforcement and device visibility. - What is RBAC in Intune?
Role-Based Access Control defines what each admin can see and do. - What are scope tags used for?
To limit visibility and delegate management by region or department. - Can I assign multiple roles to one admin?
Yes, roles can be combined for broader permissions.
- What is Endpoint Protection in Intune?
It’s a set of security policies to protect devices from threats. - What platforms are supported?
Windows, macOS, iOS/iPadOS, and Android. - What are security baselines?
Predefined Microsoft templates for enforcing best practices. - Can I manage antivirus settings with Intune?
Yes, you can configure Microsoft Defender Antivirus policies. - Does Intune support disk encryption?
Yes, you can enforce BitLocker for Windows and FileVault for macOS. - Can I block USB or camera access?
Yes, via device restriction policies under Endpoint Security.
Next Steps:
Explore free labs at
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/intune-service/
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/intune-service/fundamentals/what-is-intune