Introduction to Microsoft Intune – The Complete Beginner Guide
What Is Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based service from Microsoft that helps IT administrators manage, secure, and protect company-owned or employee devices (called endpoints) and applications from anywhere in the world using just a web browser. Unlike traditional on-premises tools that require physical servers and complex setups, Intune runs entirely in the Microsoft Azure cloud, making it scalable, cost-effective, and accessible 24/7 without hardware maintenance. It’s part of Microsoft’s modern management approach and works closely with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), Microsoft Defender, and Microsoft 365.
- Simple definition: Intune is the “remote control” and “rules engine” for company devices and apps.
- Key goal: Protect company data while keeping the user experience smooth.
- Modern management: Policies and apps are delivered via the internet—no domain join, VPN, or imaging required in most scenarios.
Why Microsoft Created Intune
In the past:
- Employees worked only from offices
- Devices were connected to company networks
- IT teams could physically touch devices
Today:
- Employees work remotely
- Devices are used from home, cafes, airports
- Personal phones are used for work
Hence, Microsoft Intune was created to solve modern workplace challenges.
Why organizations choose Intune
- Cloud-native scale: No servers to build or patch; globally available.
- Zero Trust alignment: Verify explicitly; enforce least privilege; assume breach.
- BYOD support: Secure corporate data on personal devices without taking over the device.
Cost and agility: Faster onboarding, reduced imaging, centralized management.
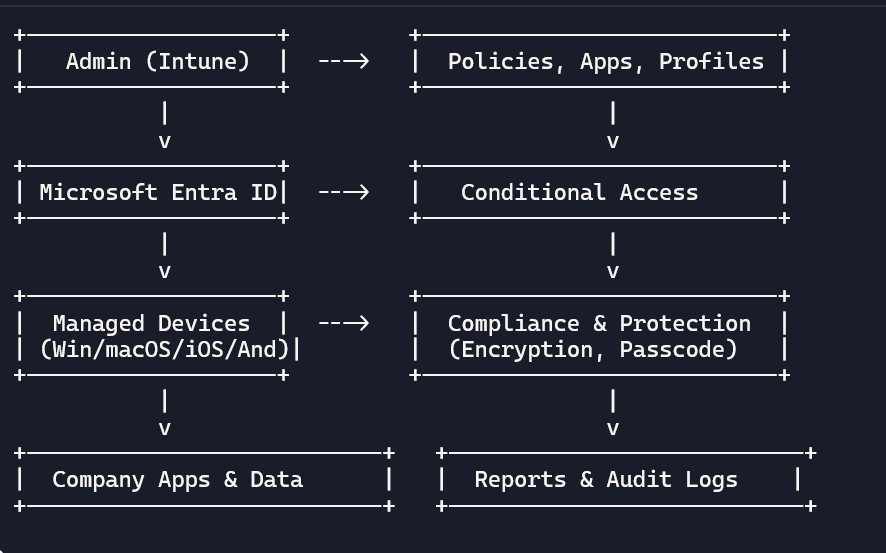
What Intune manages
- Devices: Windows, macOS, iOS/iPadOS, Android (personal or corporate).
- Apps: Microsoft 365 apps, line-of-business apps, store apps, web links.
- Policies: Configuration (Wi-Fi, VPN, certificates), compliance (passwords, encryption), protection (App Protection Policies), and security baselines.
- Access: Conditional Access integrates with Entra ID to allow/deny based on compliance, risk, and context.
Core Functionality Breakdown
Intune handles three main pillars: Device Management (enrolling and configuring laptops, phones, tablets), App Management (deploying and securing business apps), and Security & Compliance (enforcing rules to protect data). It supports all major platforms: Windows 10/11, macOS, iOS/iPadOS, Android, and even Linux in preview modes.
- Device Enrollment Process: Devices register with Intune via a simple app or web portal. Once enrolled, IT can push updates, install software, or remotely wipe data.
- Policy Enforcement: Rules like “require screen lock after 5 minutes” or “block unapproved apps” apply automatically.
- Zero-Touch Deployment: New devices auto-configure during first boot using Apple DEP or Android Zero-Touch for enterprises.
Intune’s place in the Microsoft ecosystem
- Microsoft Entra ID: Identity, device registration, Conditional Access, and user/group targeting.
- Microsoft 365: Outlook, Teams, OneDrive management and protection.
- Microsoft Defender: Threat signals, endpoint security, and MDM/MAM integrations.
- Graph API & PowerShell: Automation, reporting, and integration with external systems.
Real-world example scenarios
- Scenario 1 – New joiner onboarding: HR creates the user → Account is licensed → User signs into Windows and is auto-enrolled → Required apps and policies deploy → Device becomes compliant → Access granted to company resources.
- Scenario 2 – Lost phone: Admin finds the device in Intune → Issues a selective wipe → Corporate data removed while personal data remains.
- Scenario 3 – Remote workforce: Devices enroll from home → Wi-Fi/VPN profiles, certificates, and apps deploy automatically → Compliance plus Conditional Access ensures only healthy devices can access data.
Typical workflows in Intune
- Plan → Enroll → Configure → Protect → Monitor → Remediate.
Policy lifecycle: Create → Assign to groups/filters → Monitor → Update → Retire
Terms you’ll see often
- MDM (Mobile Device Management): Device-level management via enrollment.
- MAM (Mobile Application Management): App-level protection without device enrollment (often BYOD).
- Compliance policies: Rules devices must meet (e.g., encryption enabled).
- App protection policies (APP): Control copy/paste, saving, and data leakage in apps.
- Security baselines: Predefined Microsoft policy templates for Windows and Edge.
- Filters: Target policies to devices with dynamic attributes (e.g., OS == Android).
- Policy sets: Bundle policies, apps, and profiles for repeatable deployments.
- Co-management: Manage Windows devices with both ConfigMgr (SCCM) and Intune.
Beginner checklist
- Understand your device mix: Windows, macOS, iOS/iPadOS, Android.
- Identify management style: MDM (corporate) vs. MAM (BYOD).
- Define data protection goals: What must be protected and how.
- License appropriately: Ensure users/devices have needed Microsoft 365/EMS licenses.
- Start small: Pilot with a small group before scaling.
FAQ Section:
- Q: Can I use Intune for personal devices? A: Yes, via BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) with app protection policies that secure company data without touching personal files.
- Q: What’s the difference from SCCM? A: SCCM is on-premises for large networks; Intune is cloud-native, hybrid possible via co-management.
Next Steps
Explore free labs at
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/intune-service/
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/intune-service/fundamentals/what-is-intune